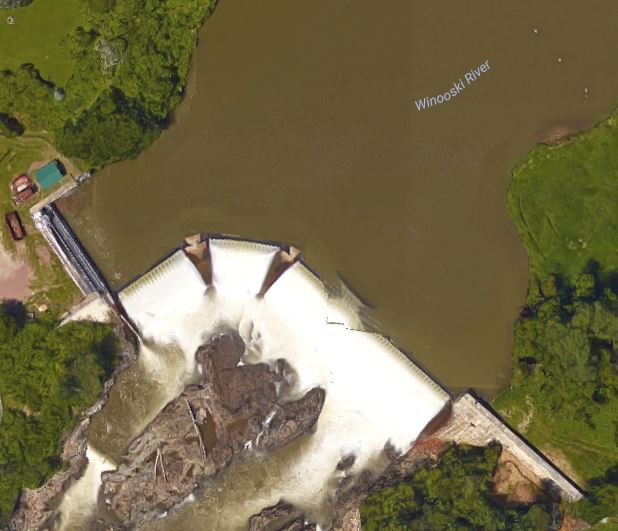
The hydroelectric dam in the study. Turbine intakes and bypass entrances to the left, open spill gates to the right. Photo from Google Maps.
The paper “Migratory delay leads to reduced passage success of Atlantic salmon smolts at a hydroelectric dam” by Daniel Nyqvist (Kau), Larry Greenberg (Kau), Elsa Goerig (INRS, Quebec) , Olle Calles (Kau) , Eva Bergman (Kau), William Ardren (US Fish and Wildlife), and Theodore Castro-Santos (USGS) was recently published in the journal Ecology of Freshwater Fish. The paper presents a study on the behavior of landlocked Atlantic salmon smolts in the Winooski River in Vermont, USA.
In the abstract the authors write:“Passage of hydropower dams is associated with mortality, delay, increased energy expenditure and migratory failure for migrating fish and the need for remedial measures for both upstream and downstream migration is widely recognized. A functional fish passage must ensure safe and timely passage routes that a substantial portion of migrating fish will use. Passage solutions must address not only the number or percentage of fish that successfully pass a barrier, but also the time it takes to pass. Here we used radio telemetry to study the functionality of a fish bypass for downstream-migrating wild-caught and hatchery-released Atlantic salmon smolts. We used time to event analysis to model the influence of fish characteristics and environmental variables on the rates of a series of events associated with dam passage. Among the modeled events were approach rate to the bypass entry zone, retention rates in both the forebay and the entry zone and passage rates. Despite repeated attempts, only 65% of the tagged fish present in the forebay passed the dam. Fish passed via the bypass (33%), via spill (18%) and, via turbines (15%). Discharge was positively related to approach, passage, and retention rates. We did not detect any differences between wild and hatchery fish. Even though individual fish visited the forebay and the entry zone on multiple occasions, most fish passed during the first exposures to these zones. This study underscores the importance of timeliness to passage success and the usefulness of time to event analysis for understanding factors governing passage performance.”
Read the abstract and access the paper here. If you don’t have access to the journal’s content, email any of the authors.